Functions & Graphing Calculator \square!See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading the graph of y=f (x) is shown below Graph y=1/2f (x)Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!
Answered Use The Graph Of Y F X Below To Graph Bartleby
How to graph f(x y) functions
How to graph f(x y) functions-If it's a linear equation, a straight line, then the equation is y= (1/2)x 3 y = mx b is a linear function in slope intercept form (0,3) is the y intercept or y=3 = b y = slope times x y coordinate of the y intercept y = (1/2)x 3 or 2y = x 6, if you want to eliminate the fraction by multiplying by 2 Upvote • 0 DownvoteAnswer choices multiply the x 2 by a fraction multiply the x 2 by a decimal multiply the x 2 by a negative number multiply the x 2 by a number greater than 1



Exponential Functions
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!The rule replacing x by x in the right side of the equation for f(x) results in a reflection of the graph into (or across) the yaxis y = f(x1)1 If the red graph below is of f(x) Then the green graph below is f(x1) 1 Two things were done to f(x) First x was replaced by (x1) which moves the graph LEFT by 1 unit That is y = f(x1) would have looked like this Rule Replacing x by xp moves the graph p unit left Replacing x by xp moves the graphThus, the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote The equation d d x e x = e x {\displaystyle {\tfrac {d}{dx}}e^{x}=e^{x}} means that the slope of the tangent to the graph at each point is equal to its y coordinate at that point
Absolute Value and DistanceF is () for x>1 ;Looking at we can see that the equation is in slopeintercept form where the slope is and the yintercept is Since this tells us that the yintercept is Remember the yintercept is the point where the graph
D) Since the points on the graph y = f (2 x) relate to the graph of f (x) by (x, y) → 1, 2 x y , the zeros will occur at x = –2 and x = 15 Section 12 Page 31 Question 15 The graph of a function y = f (x) is contained completely in quadrant IV a) A transformation to y = – f (x) represents a reflection in the xaxis (x, y) → (x, – y)Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;The symbol f(x), which is often used to name an algebraic expression in the variable x, can also be used to denote the value of the expression for specific values of x For example, if f(x) = 2x 4 where f{x) is playing the same role as y in Equation (2) on page 285, then f(1) represents the value of the expression 2x 4 when x is




If The Graph Of The Function Y F X Is As Shown The Graph O



Search Q Vertical Stretch Tbm Isch
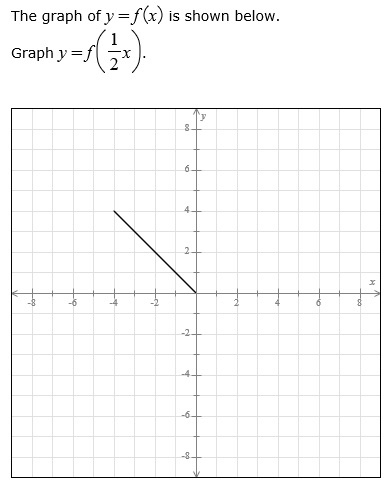
Video Transcript Okay, So we are going to use why equals f of X to help us graph this equation So we have f of 1/2 X And because the one happens next to the X, that tells us that we're going to divide all of our X coordinates by 1/2 Or multiply that by two because you have to multiply about the reciprocal which is toNow plot the points and compare the graphs of the functions g and h to the basic graph of f (x) = x 2, which is shown using a dashed grey curve below The function g shifts the basic graph down 3 units and the function h shifts the basic graph up 3 units In general,Example 1 Fig 1 is the graph of the parabola f ( x) = x2 − 2 x − 3 = ( x 1) ( x − 3) The roots −1, 3 are the x intercepts Fig 2 is its reflection about the xaxis Every point that was above the x axis gets reflected to below the x axis And every point below the x axis gets reflected above the x




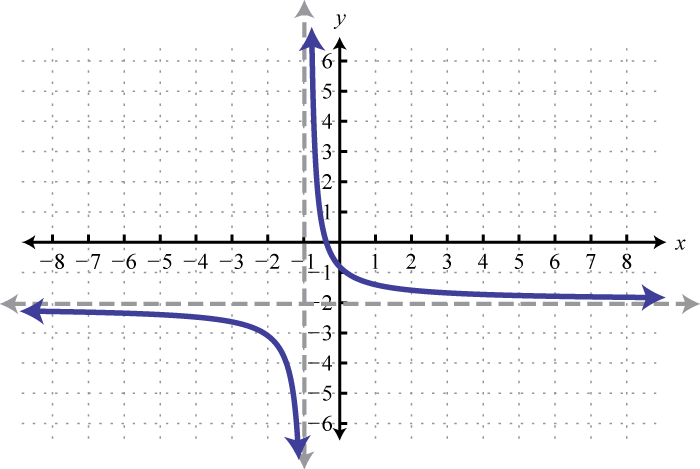
The Characteristics Of The Graph Of A Reciprocal Function Graphs And Functions And Simultaneous Equations




Vocabulary L L L The Function Fx X
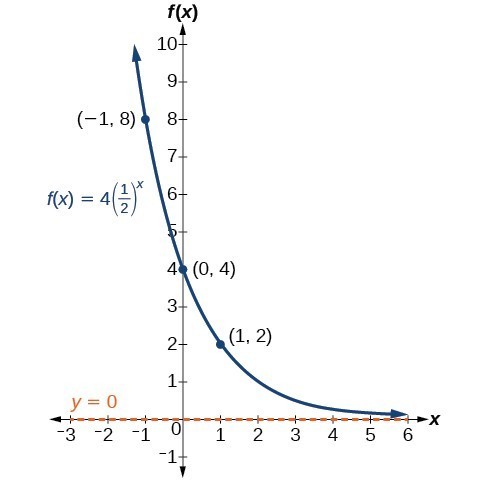
The graph of an exponential function is a strictly increasing or decreasing curve that has a horizontal asymptote Let's find out what the graph of the basic exponential function y = a x y=a^x y = ax looks like (i) When a > 1, a>1, a > 1, the graph strictly increases as xQuestion 1516 Graph y = (1/2)x 1 Answer by jim_thompson5910 () ( Show Source ) You can put this solution on YOUR website! method 1 You can use the formula x = −b ±√b2 −4ac 2a to determine the xintercepts Find the mid point and that is the x coordinate for the minimum Substitute back into the equation to determine the y coordinate method 2 not very well known or used Start the process of completing the square (you do not need to do all of it)



Domain And Range Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions




Given The Graph Of F X Below Sketch A Graph Of The Transformation Y Frac 1 2 F X 4 Study Com
Y=x is a graph V shaped where the vertex of V is the origin So Now we will be doing origin shifting for y=x1 Say x1=X so y=X Now for y vs X graph, our graph will be a V with vertex of V at origin But Hey!F is () for xGeometrically, the equation y = f(x) represents a curve in the twodimensional (x;y) plane, and we call this curve the graph of the function f(x) 02 Functions of two variables Our aim is to generalise these ideas to functions of two variables Such a function would be written as z = f(x;y)



What Is A Function Transformation Expii



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
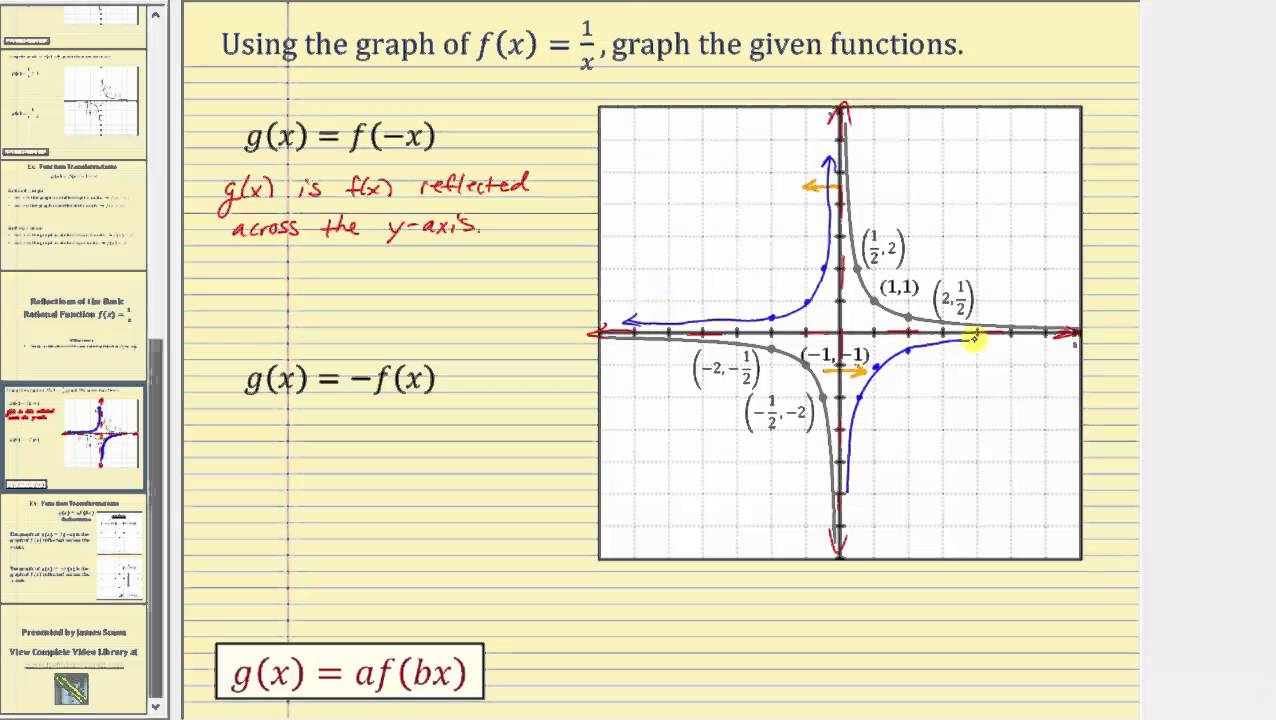
11 Uni Grad 17 #4 Try experimenting with an original graph Note that the f (x) is the y value of that original graph Substitute that y value into 1/f (x), and then you will see that 1/f (x) is a reciprocal function Also, note that if at a point, f (x) = 1, then 1/f (x), We know that X=x1, so forFor curved surfaces, the situation is a little more complex Let f (x) f (x) be a nonnegative smooth function over the interval a, b a, b We wish to find the surface area of the surface of revolution created by revolving the graph of y = f (x) y = f (x) around the xaxis xaxis as shown in the following figure



Graphing Reflections Of The Basic Rational Function F X 1 X Youtube



Draw The Graph Of Y 1 1 X
Y= 1/2 x \square!D The first figure of the Sierpinski triangle has one shaded triangle The second figure of the Sierpinski triangle has three shaded triangles B y = (1/2)e^x What are the domain and range of f(x) = 2(3^x) A Which graph represents the function g(x) = Ix 4I 2 AGet the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlpha



Exponential Functions



Sat Math Graph Example 2 Sat Math Forbest Academy
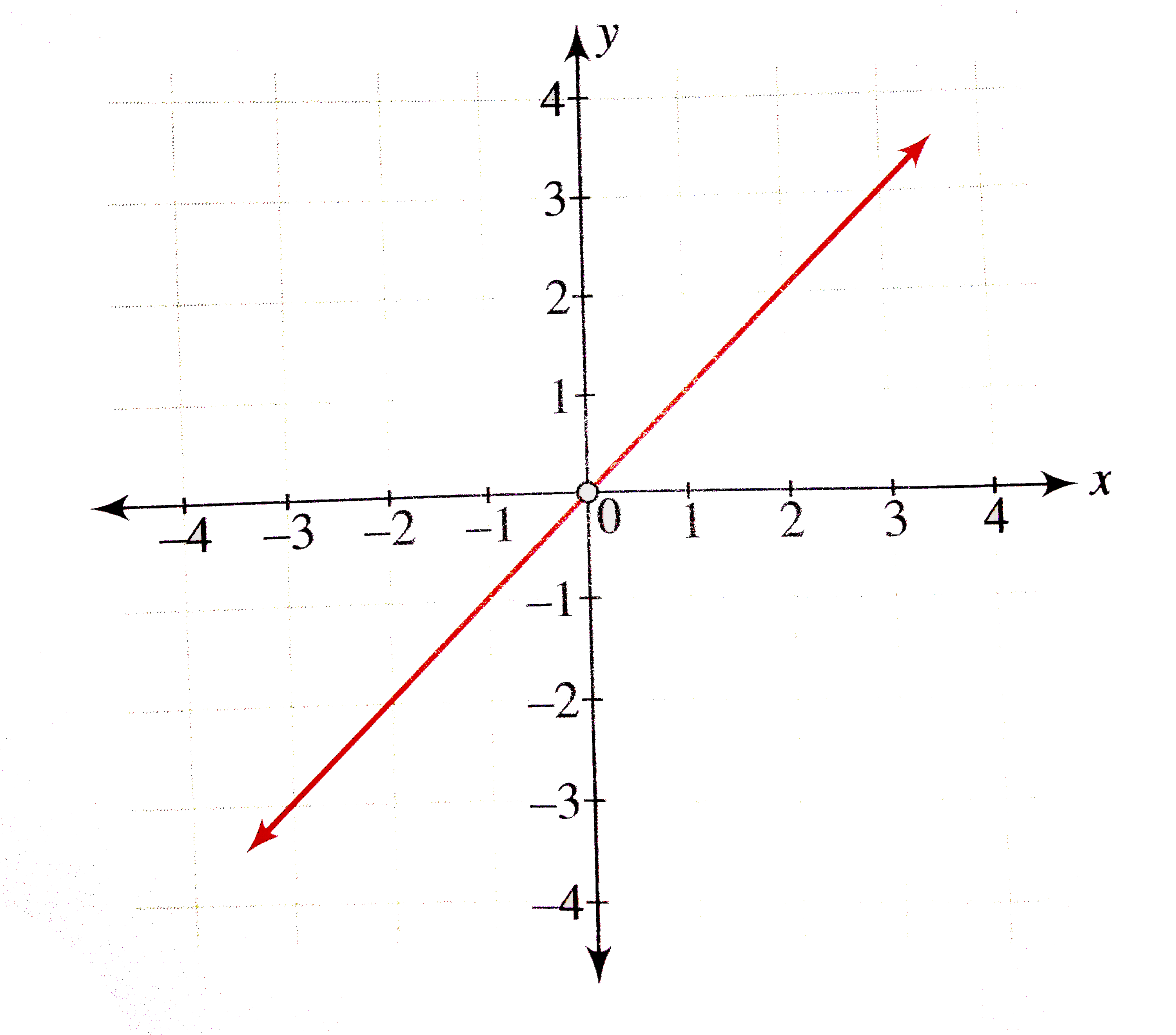
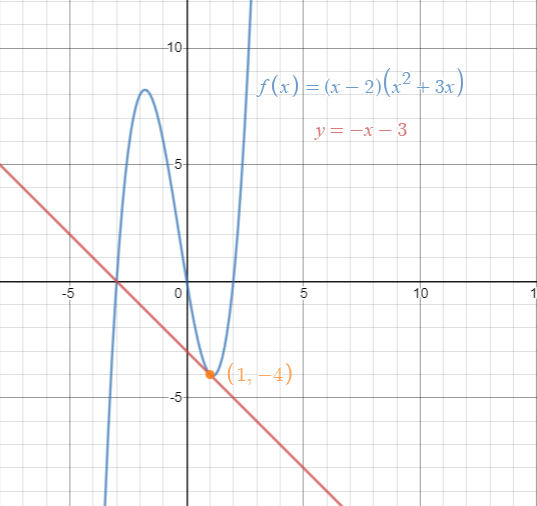
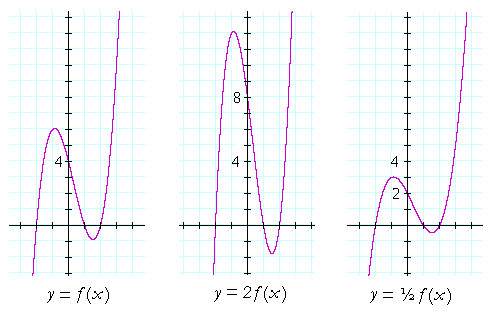
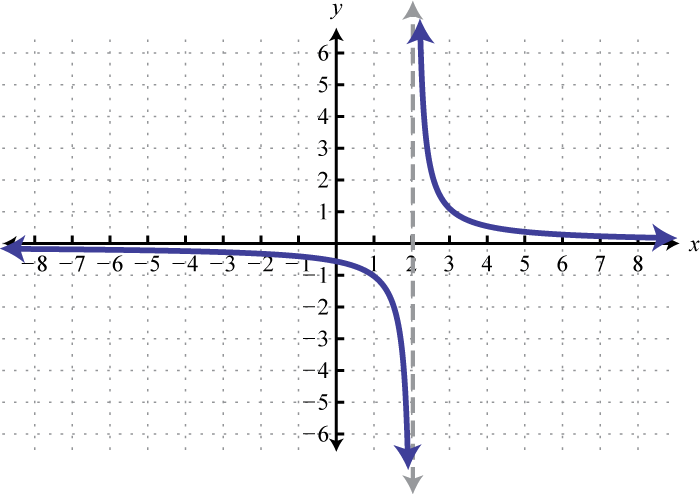
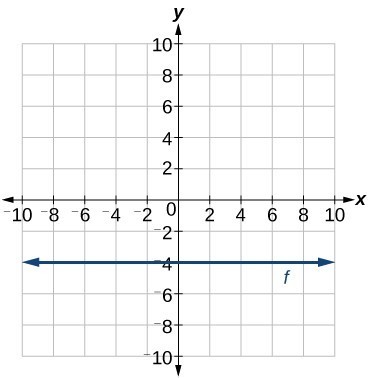
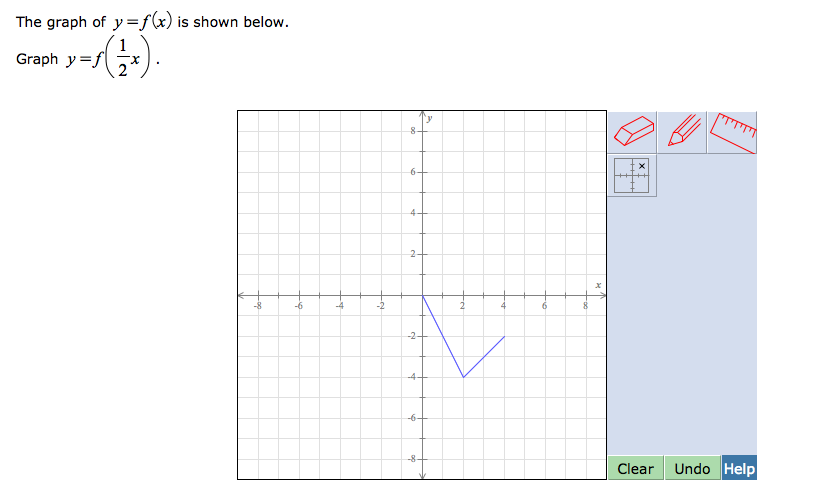
About Beyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expectExample 1 Find the x and the y intercepts of the graph of function f defined by f(x) = 3 x 9 Solution to Example 1 Since a point on the y axis has x coordinate equal to zero, to find the y interecpt, we set x to zero and find the y coordinate which is f(0) f(0) = 3(0) 9 = 9 A point on the x axis has y coordinate equal to 0, to find the x intercept, we set y = f(x) = 0 and solve for x Macailah H asked • The graph of y=f (x) is shown below Graph y=1/2f (x) The grap is a partial line , showing to be negative The yint is 3 and the slope is 1/2 Follow • 1 Add comment More



Solved Describe How You Would Graph The Equation Of The Line Y 1 5x 3 Using The Slope Intercept Form Course Hero



If The Graph Of The Function Y F X Is As Shown Then The Graph Of Y 1 2 F X F X Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
The graph always lies above the xaxis, but becomes arbitrarily close to it for large negative x;Cos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering To zoom, use the Answer The graph is attached below Stepbystep explanation y – 1 = 2 (x – 2) y1 = 2x 4 add 1 on both sides y = 2x 3 To graph the given equation we make a table Plug in some number for x and find out the value of y



Using Transformations To Graph Functions



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Chegg Com
Drawing graphs of y=1/f(x) and y=I1/f(x)I from y=f(x) New Resources Types of Triangle & Sum of angle of Triangle; So if y=1/2x, then x=2y graph{1/2(x) 10, 10, 5, 5} It's best to only plot whole numbers because then your line will be perfectly straight If you plot 2 for x, then plug 2 into the equation 2=2y Then solve y=1 So the first coordinate would be (2,1) Just continue that and you'll be good!Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history
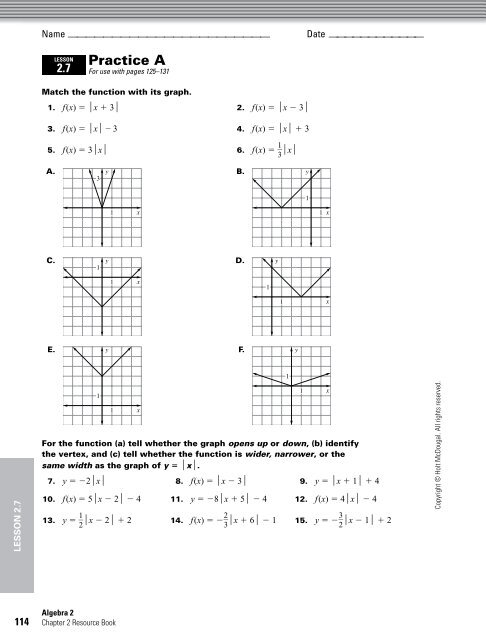



Practice Mathnmind



A Find An Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Graph Of F At The Given Point B Use A Graphing Utility To Graph The Function And Its Tangent Line At The
Function Grapher is a full featured Graphing Utility that supports graphing up to 5 functions together You can also save your work as a URL (website link) Usage To plot a function just type it into the function box Use "x" as the variable like this Examples sin(x) 2x−3;Translations The graph of a function can be moved up, down, left, or right by adding to or subtracting from the output or the input Adding to the output of a function moves the graph up Subtracting from the output of a function moves the graph down Here are the graphs of y = f (x), y = f (x) 2, and y = f (x) 2The graph of f(x) in this example is the graph of y = x 2 3 It is easy to generate points on the graph Choose a value for the first coordinate, then evaluate f at that number to find the second coordinate The following table shows several values for x and the function f evaluated at those numbers x 2 1 0 1 2 f(x)



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
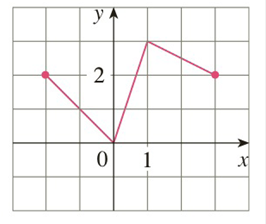



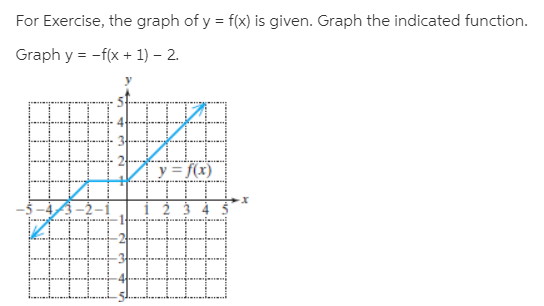
The Graph Of F Is Given Draw The Graphs Of The Following Functions A Y F X 3 B Y F X 1 C Y 1 2 F X D Y F X Bartleby
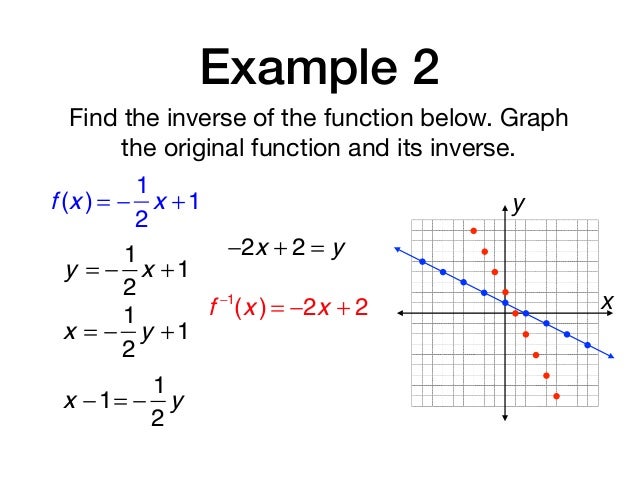
How does the graph of g(x) = 3^x 2 compare to the graph of f(x) = 3^x ?Suppose I want to find the value of the second function at x = 2 To do this I find the value of the first function at x = 2 5Algebra Graph y=1/2f (x) y = 1 2 f (x) y = 1 2 f ( x) Graph y = 1 2 ⋅f (x) y = 1 2 ⋅ f ( x)




Ch1 Graphs Y Axis X Axis Quadrant I Quadrant Ii Quadrant Iii Quadrant Iv Origin 0 0 6 3 5 2 When Distinct Ppt Download




The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 Over 2 F X Study Com
Starting at y=2f(x), click on the circle to reveal a new graph Describe the transformation Click again to remove and try the next function This problem has been solved!And it works for any fraction If your y= equation is already whole, then you're gucci!



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Of Y Chegg Com




Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver
The simplest shift is a vertical shift, moving the graph up or down, because this transformation involves adding a positive or negative constant to the function In other words, we add the same constant to the output value of the function regardless of the input For a function g ( x) = f ( x) k \displaystyle g\left (x\right)=f\left (xGraph f(x) = −2x 2 3x – 3 a = −2, so the graph will open down and be thinner than f(x) = x 2 c = −3, so it will move to intercept the yaxis at (0, −3) Before making a table of values, look at the values of a and c to get a general idea of what the graph should look likeGraph y= (1/2)^x y = ( 1 2)x y = ( 1 2) x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0 Horizontal Asymptote y = 0 y = 0



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Chegg Com



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations
C < 0 moves it down We can move it left or right by adding a constant to the xvalue g(x) = (x If the graph of the function `y = f(x)` is as shown Its graph is shown below From the side view, it appears that the minimum value of this function is around 500 A level curve of a function f (x,y) is a set of points (x,y) in the plane such that f (x,y)=c for a fixed value c Example 5 The level curves of f (x,y) = x 2 y 2 are curves of the form x 2 y 2 =c for different choices of c




Answered Use The Graph Of Y F X Below To Graph Bartleby



G R A P H Y 1 2 F X Zonealarm Results
17 Transformations 123 2 to all of the xvalues of the points on the graph of y= f(x) to e ect a shift to the right 2 units Generalizing these notions produces the following resultF Graph the points obtained in parts a through e The height of the rock depends on the time, so h is the dependent variable, and t is the independent variable The points have the form (t, h) According to the graph, the rock reaches its greatest height atIf P(4,5) is a point on the graph of the function y=f(x), find the corresponding point on the graph of y=2f(x6) Hi Carl, Let me look at different functions y = g(x) and y = 4g(x 5) How do these graphs compare?
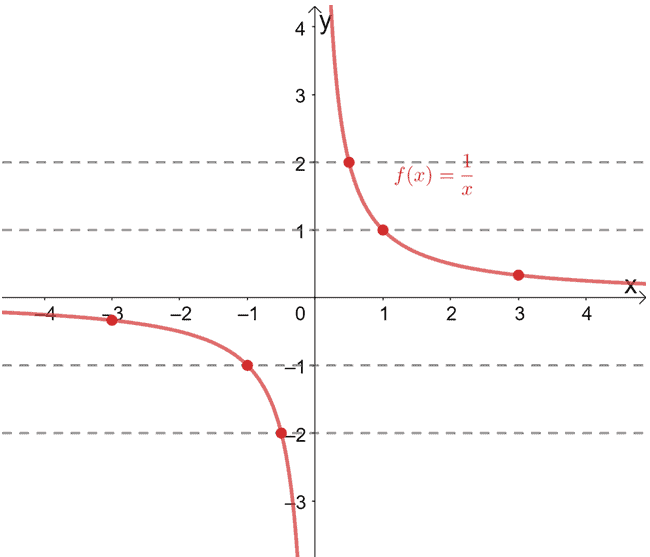



One To One Function Explanation Examples
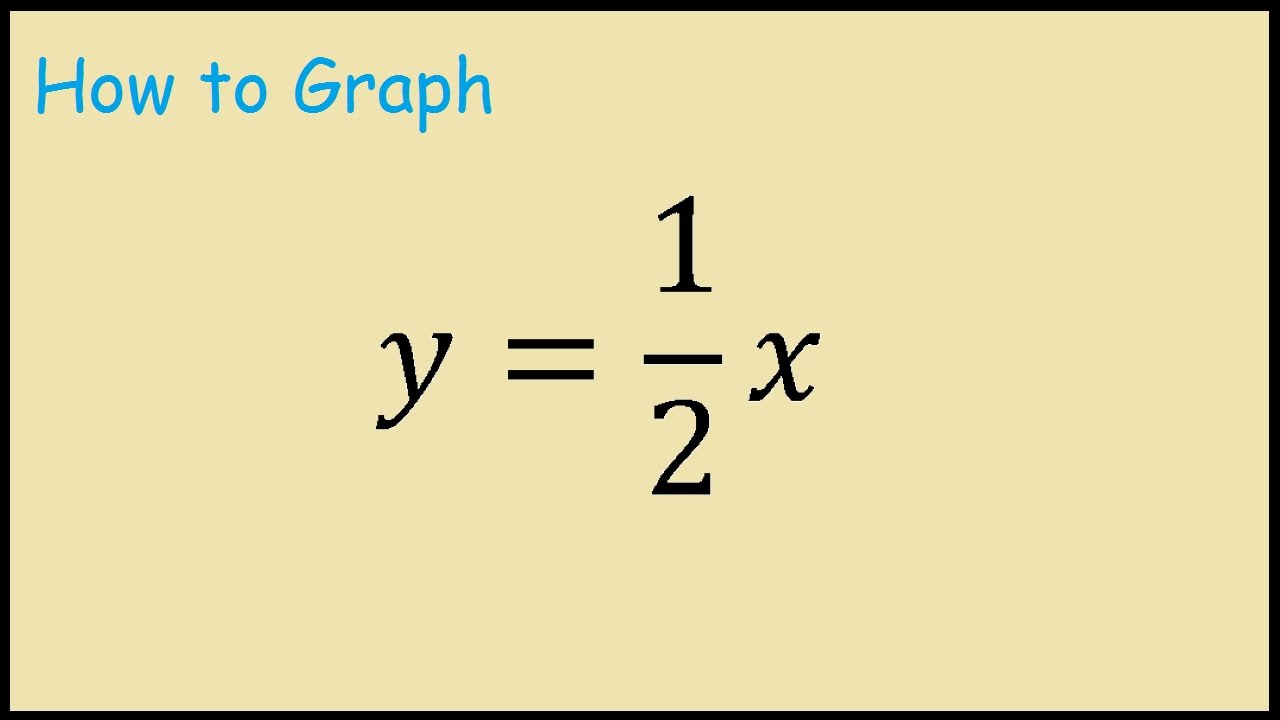



How To Graph Y 1 2x Youtube
Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources Geometry of 2x2 Matrix Multiplication with Intro QuestionsSolved The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Chegg Com For more information and source, see on this link https//wwwcheggcom/homeworkhelp/questionsandSay, y= f(x)= 1 √x Now, f(x) is defined if x belongs to 0, ∞) And for all x belonging to 0, ∞), f(x) belongs to 1,∞) So the domain of y=f(x) is 0, ∞) and the range is 1,∞) Now, y= 1 √x can be represented as x²=(y1), provided x ∈ 0,∞)



Solution Graph The Given Function By Making A Table Of Coordinates F X 2 X



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes
Textbook solution for Single Variable Calculus Early Transcendentals 8th Edition James Stewart Chapter 1 Problem 10RE We have stepbystep solutions for




Graphs And Level Curves




3 Ways To Graph A Function Wikihow




The Graph Of F Is Given Draw The Graphs Of The Following Functions A Y F X 3 B Y F X 1 C Y Frac 1 2 F X D Y




Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Video Khan Academy
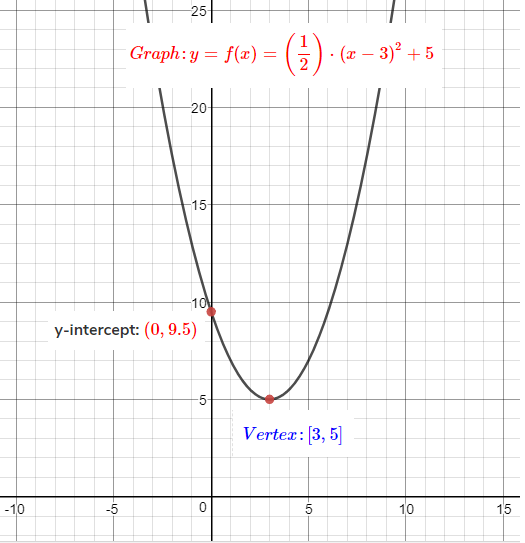



How To Graph A Parabola Y 1 2 X 3 2 5 Socratic




Me Suremen Ur Unswers The Question 1 Which Graph Represents The Function Y 3x 1 For The Domain Brainly Com
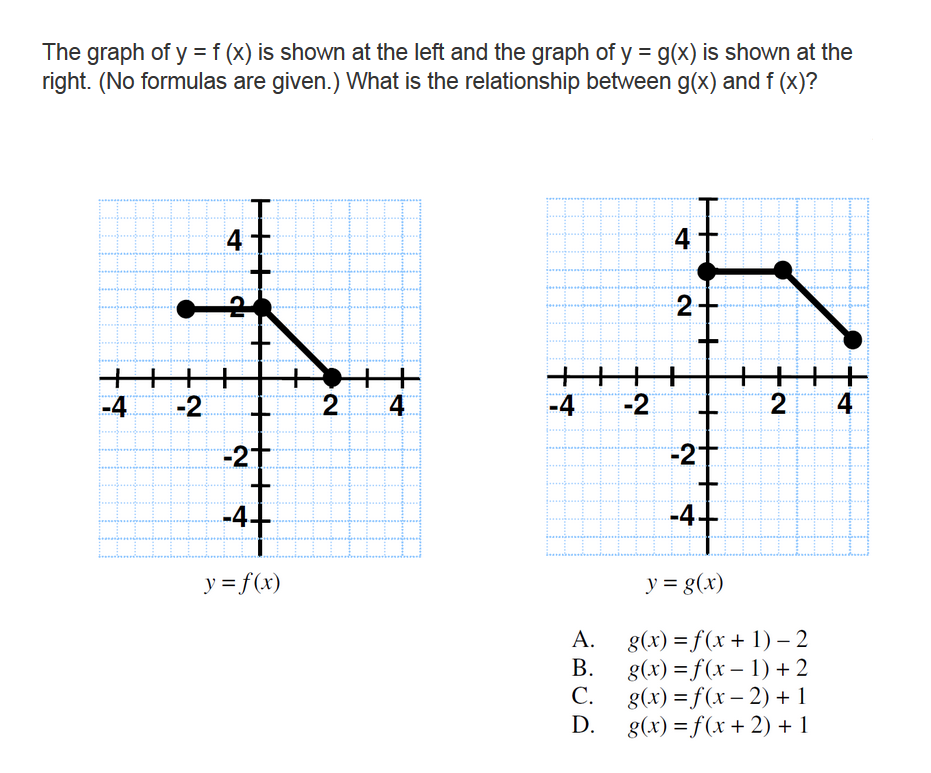



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown At The Left And The Chegg Com



What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 3 X 2 2 1 Quora



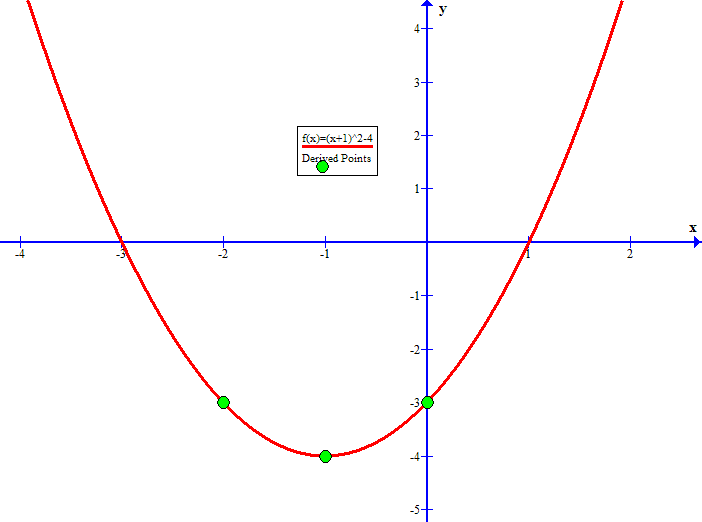
Translations Of A Graph Topics In Precalculus



1



Multiplicative Inverse Wikipedia



How Do You Graph Y X 1 2 4 Socratic
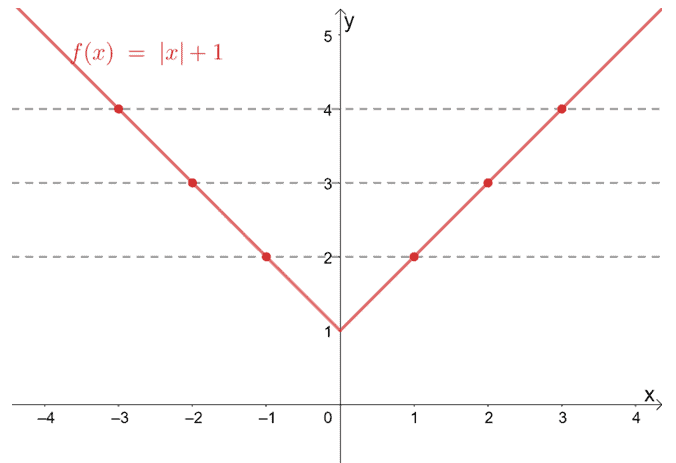



One To One Function Explanation Examples
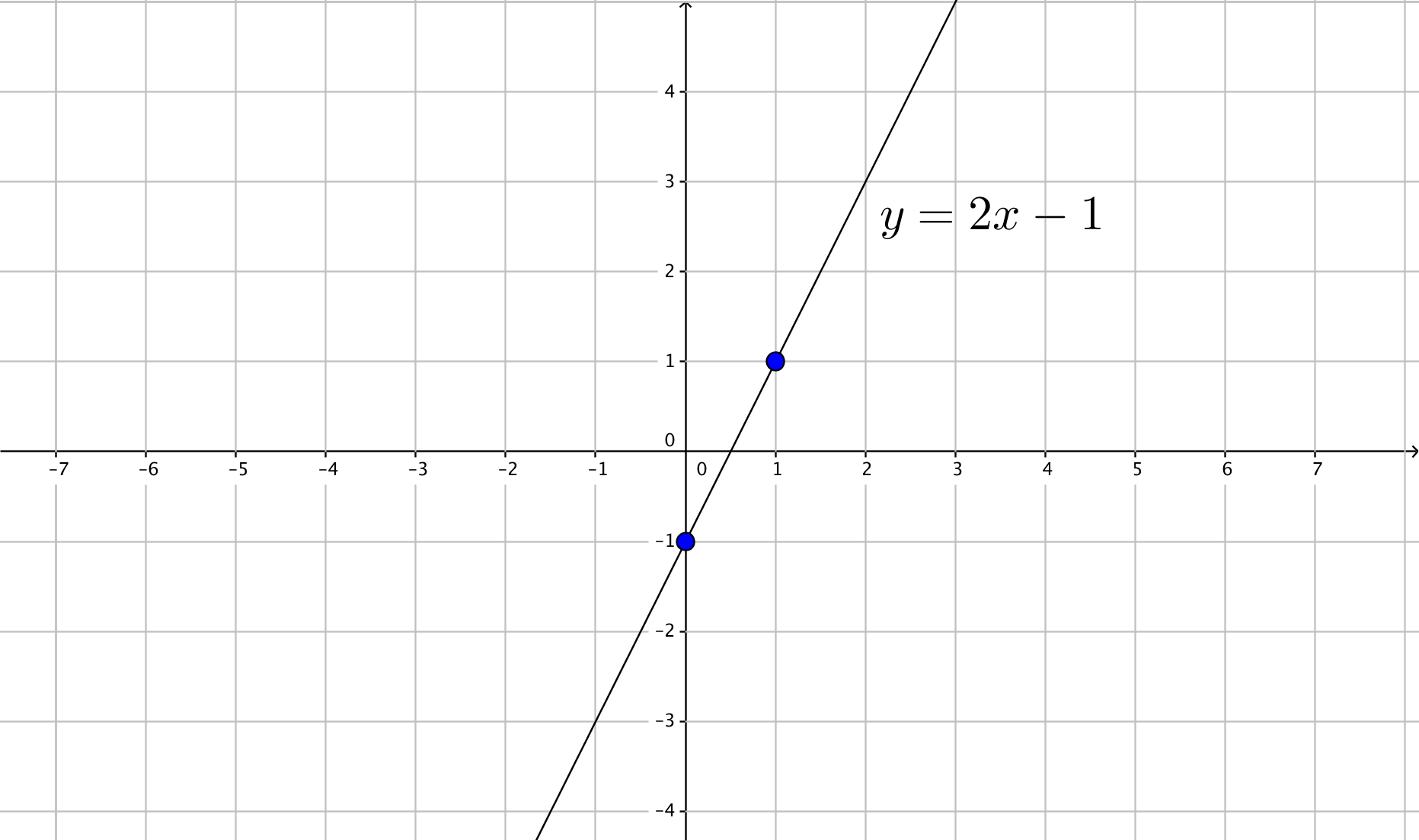



How Do You Graph Y 2x 1 By Plotting Points Socratic



Using Transformations To Graph Functions




Warm Up 1 Use The Graph Of To Sketch The Graph Of 2 Use The Graph Of To Sketch The Graph Of Ppt Download



Transformations



Answered For Exercise The Graph Of Y F X Is Bartleby




Answered For Problems 29 31 Use The Given Graph Bartleby



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra



Algebra 2 Section 5 3




Multiplicative Inverse Wikipedia



Http Tmpsantafe Org Wp Content Uploads 18 12 Graph Exp Shifts Horizontal Vertical Pdf



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
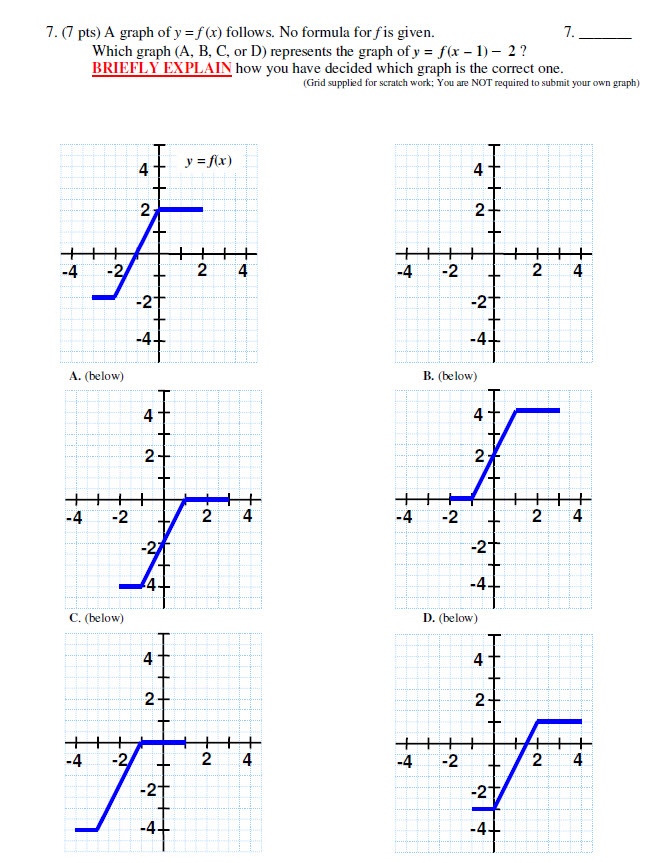



A Graph Of Y F X Follows No Formula For F Is Chegg Com



Functions Algebra Mathematics A Level Revision




Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver
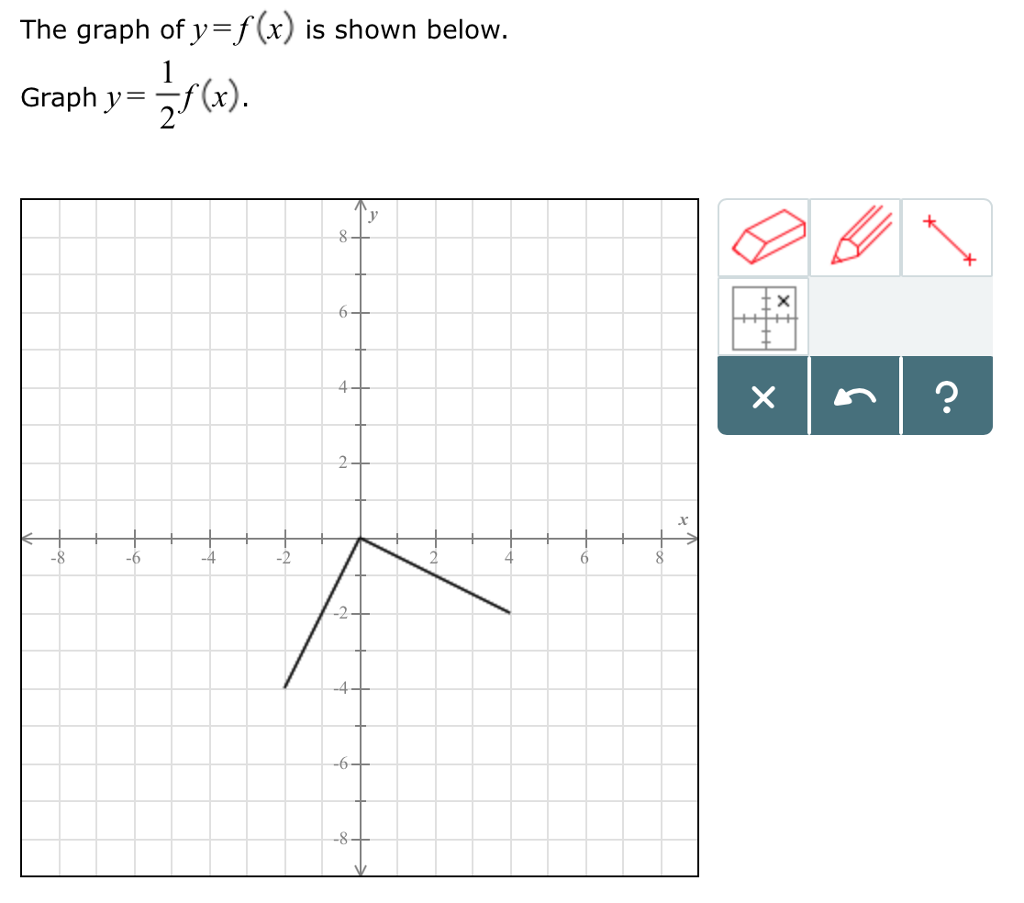



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Chegg Com



Solution Sketch The Graph Of Y 1 2x 2 2 Find The Domain Of The Function F X X 2 X 4 Find The Domain Of The Function G T 5t T 2 9 Use The Vertical Line Test To




The Graph Of Y Fx Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Fx Gauthmath



Write The Equation For A Linear Function From The Graph Of A Line College Algebra



3 2 2 Worksheet Day 2



Solved If The Point 4 7 Lies On The Graph Of 2y 2 F 1 5 X 1 What Is The Corresponding Point On The Graph Of Y F X Show Your Work Course Hero




The Graph Of Y Fx Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2 Fx Gauthmath



Horizontal Line Test For Function To Have Inverse Expii



1
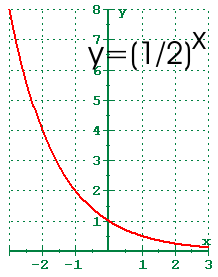



4 1 Exponential Functions And Their Graphs




The Graph Of Y F X Is Given Below Y 1 4 01 Quad 12 Then The Graph Of Y Pm F 1 X 1
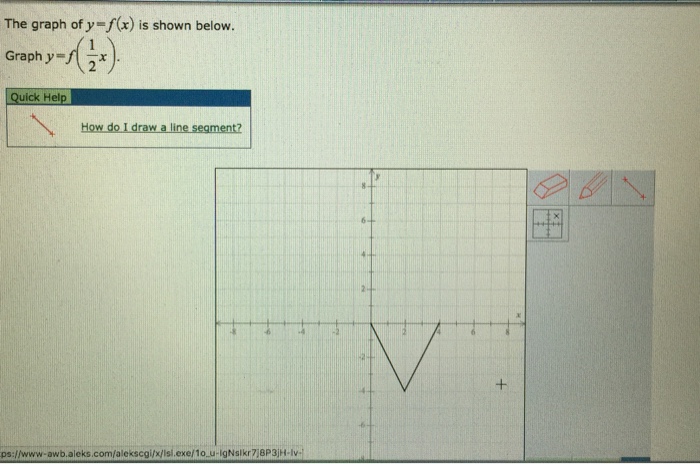



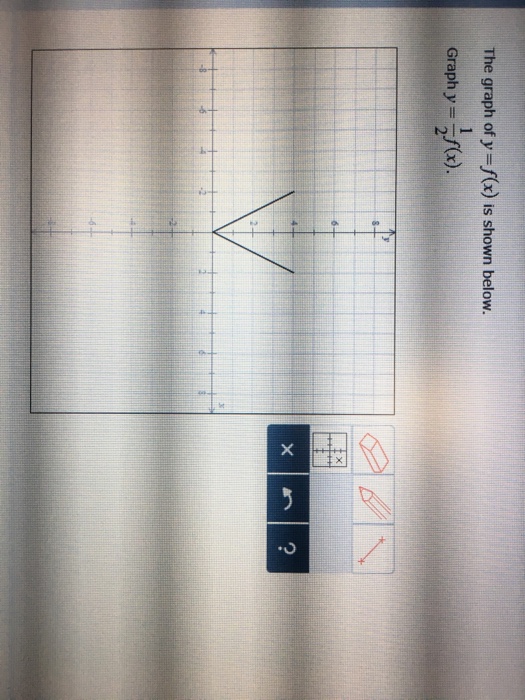
The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y F 1 2 Chegg Com



Http Www Scasd Org Cms Lib5 Pa Centricity Domain 12 Ch 2 warmup scanned key Pdf



Calcu Rigid Transformations




Which Of The Following Functions Have The Graph Symmetrical About




Use The Given Graph Of F X To Sketch A Graph Of Y 2f X Study Com



1



Graphing Square Root Functions



One Sided Limits From Graphs Video Khan Academy



Graph Transformations




The Graph Of F Is Given By Draw The Graphs Of The Following Functions A Y F X 3 B Y F X 1 C Y Frac 1 2 F X D Y F X Study Com



Http Www Mpsaz Org Rmhs Staff Lxcoleman Algebra2 Reviews Files 1 1 1 2 Algebra 2 Review Answer Key Pdf




16 5 1 Vertical Transformations Mathematics Libretexts
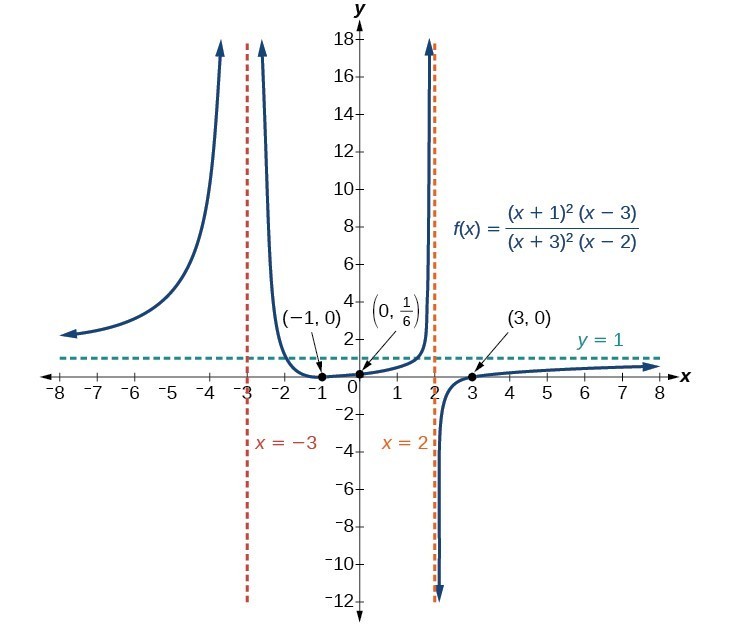



Graph Rational Functions College Algebra




If The Graph Of The Function Y F X Is As Shown The Graph O



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture01 Handout Pdf



Draw The Graph Of Y 2x 2 1 And Heance The Graph Of F X Cos



How To Draw Y 2 X 2
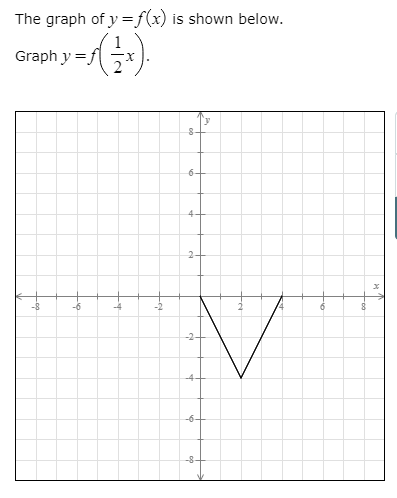



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y F 1 2 Chegg Com
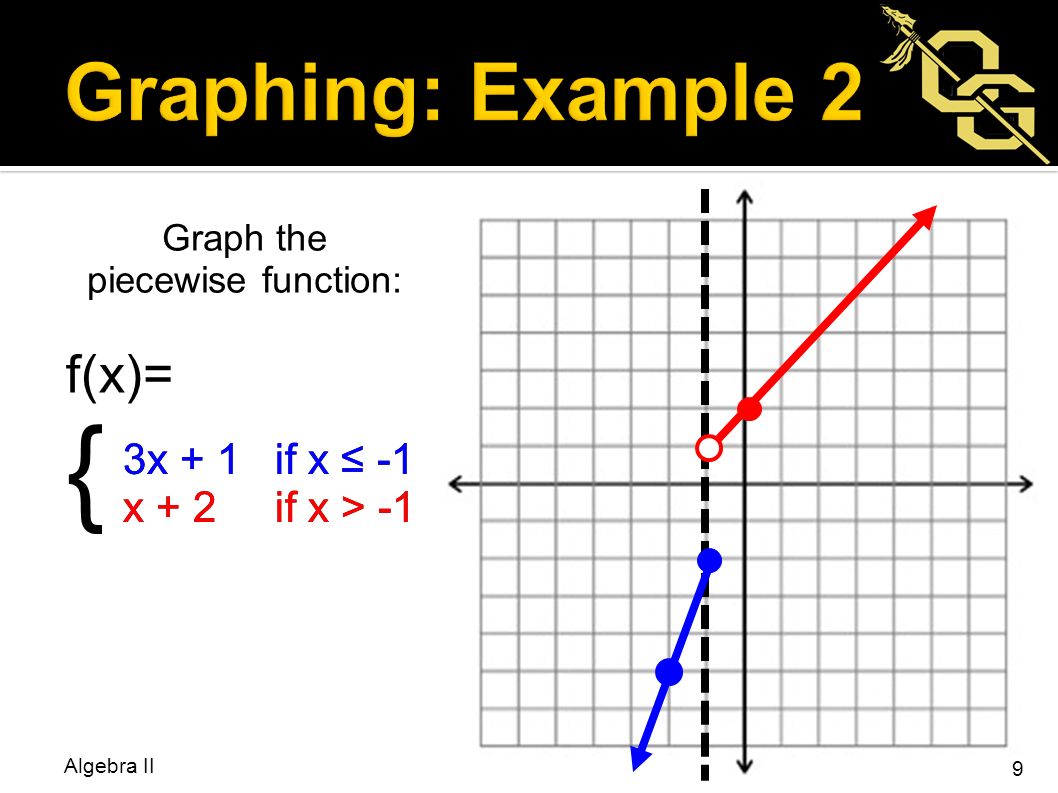



F 1 Graph




Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver
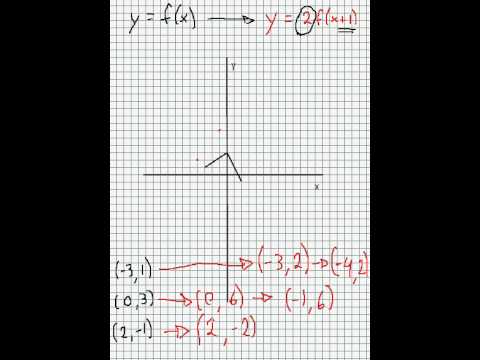



Transformation Of Graphs Y F X Into Y 2f X 1 Quick Explanation Youtube



Is F X 2x 1 Is Injective Or Surjective Quora



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes




Graphing Parabolas
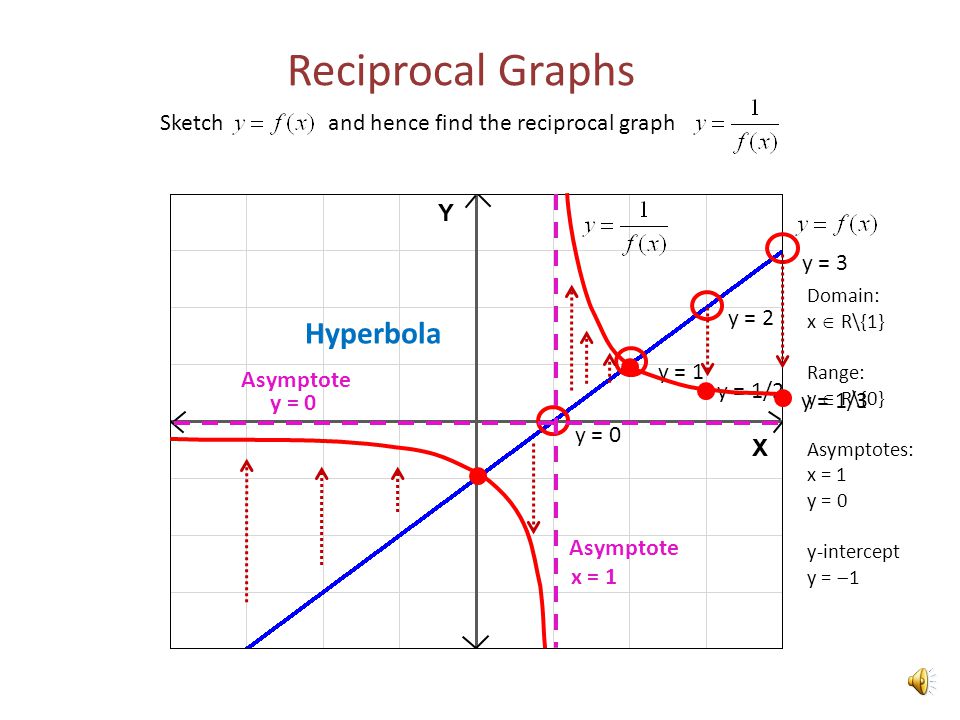



Reciprocal Graphs Sketch And Hence Find The Reciprocal Graph Y 0 Y 1 Y 2 Y 1 2 Y 3 Y 1 3 X 1 Y 0 Hyperbola Asymptote Domain X R 1 Ppt Download




Select The Correct Answer The Graph Of Function F Is Shown Function G Is Represented By The Table X Brainly Com
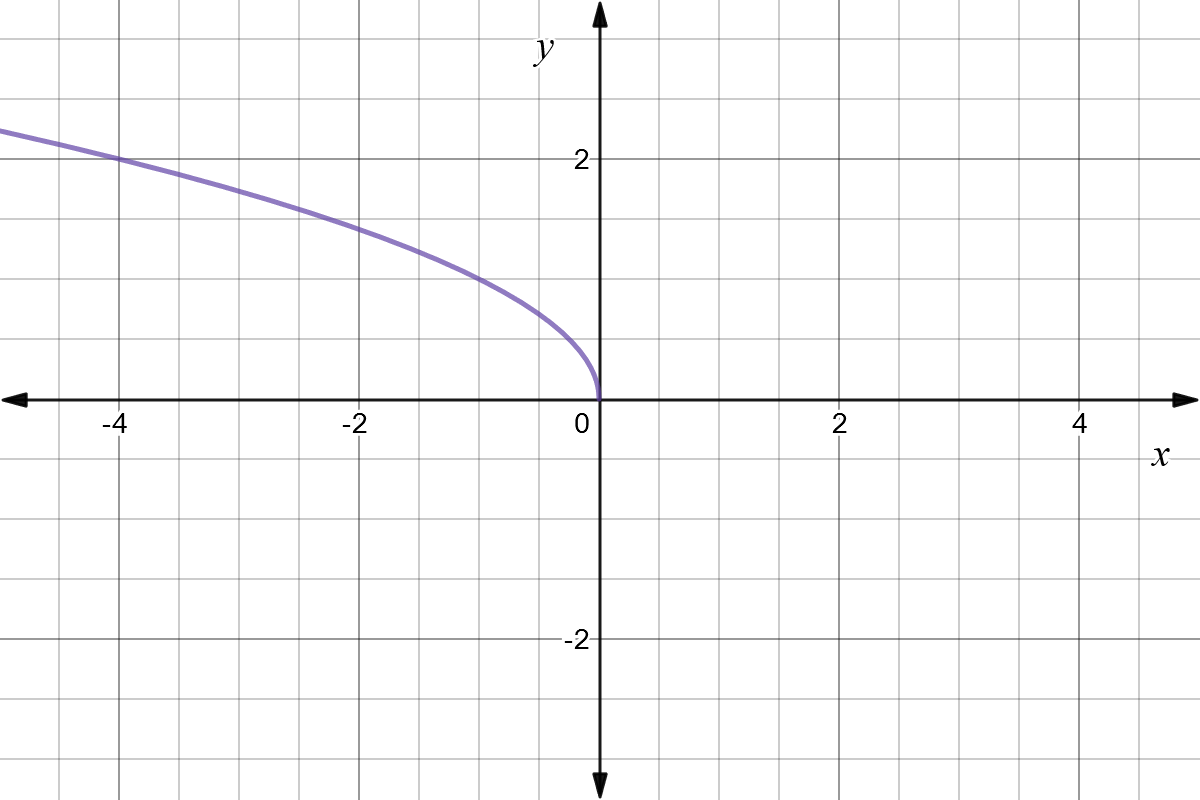



Reflect Function About Y Axis F X Expii




The Figure Above Shows The Graph Of Y Fx Which O Gauthmath
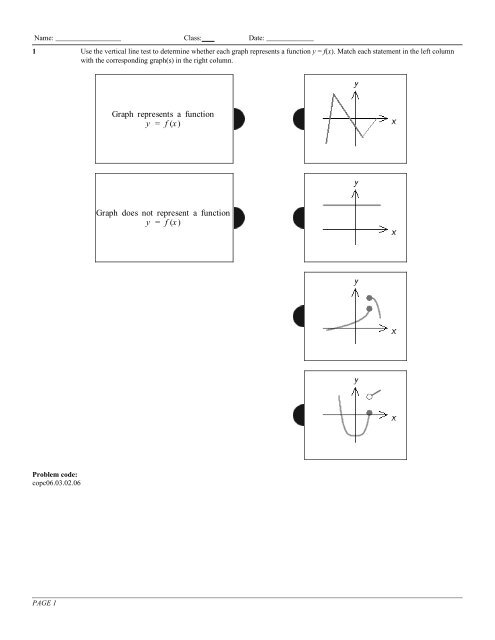



Graph Represents A Function Y F X Mathematics 1 2 3




I Need Help Asap Please The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Y 1 2f X Brainly Com



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown Below Graph Chegg Com




Graph The Linear Equation Yx 2 1 Draw




Interpret The Graph Of Frac Ax B Cx D As A Transformation Of Y Frac 1 X Mathematics Stack Exchange
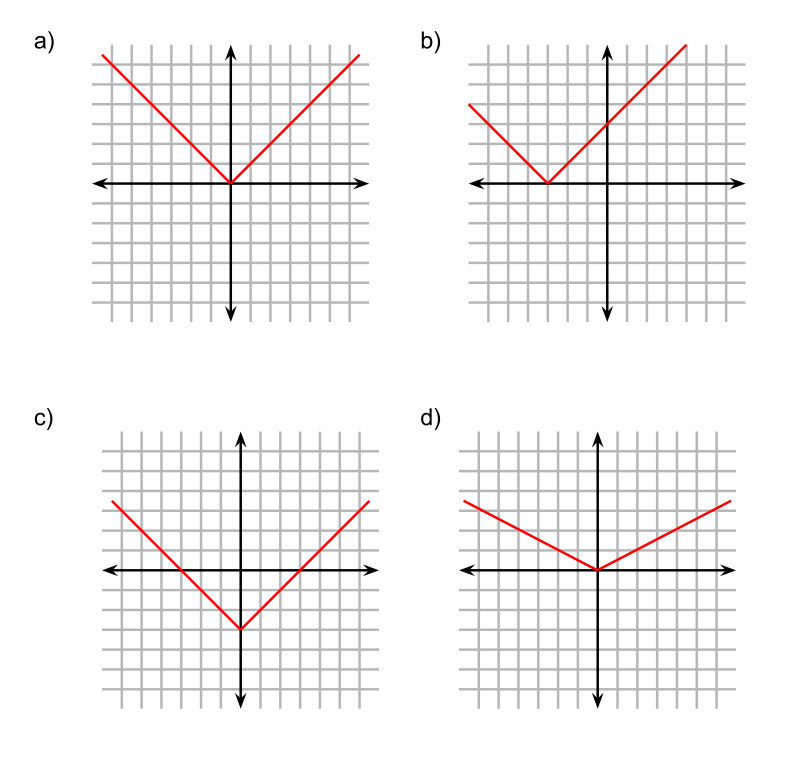



Analytic Geometry Wikiwand



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿